Gonadorelin (2 mg Vial) Dosage Protocol
Quickstart Highlights
Gonadorelin dosage supports the restoration of natural LH and FSH release from the pituitary gland, reactivating the hypothalamic‑pituitary‑gonadal (HPG) axis[1]. As a synthetic form of gonadotropin‑releasing hormone (GnRH), gonadorelin stimulates testosterone production in men and promotes ovulation in women when administered in short, pulsatile doses[2][3]. This educational protocol outlines a subcutaneous micro‑dosing approach using a practical dilution for accurate insulin‑syringe measurements.
- Reconstitute: Add 2.0 mL bacteriostatic water → 1 mg/mL concentration (1000 mcg/mL).
- Typical dose range: 50–250 mcg per injection, 2–3 times weekly.
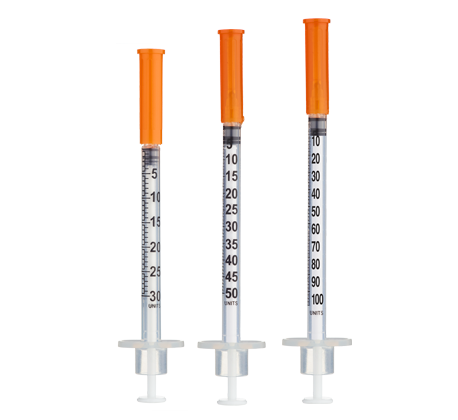
- Easy measuring: At 1 mg/mL, 1 unit = 0.01 mL = 10 mcg on a U‑100 insulin syringe.
- Storage: Lyophilized: store at −20 °C (−4 °F); after reconstitution, refrigerate at 2–8 °C (35.6–46.4 °F); avoid freeze–thaw cycles.

Dosing & Reconstitution Guide
Educational guide for reconstitution and periodic dosing
Standard / Maintenance Approach (2 mL = 1 mg/mL)
Route: Subcutaneous injection. Frequency: 2–3 times per week on non‑consecutive days (e.g., Mon/Wed/Fri or Tue/Thu/Sat).
| Week/Phase | Dose per Injection (mcg) | Units (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Weeks 1–2 (Initiation) | 50 mcg | 5 units (0.05 mL) |
| Weeks 3–4 (Titration) | 100 mcg | 10 units (0.10 mL) |
| Weeks 5–8 (Maintenance) | 100–150 mcg | 10–15 units (0.10–0.15 mL) |
For ≤10‑unit (≤0.10 mL) administrations, consider 30‑ or 50‑unit insulin syringes for improved readability.
Reconstitution Steps
- Draw 2.0 mL bacteriostatic water with a sterile syringe.
- Inject slowly down the vial wall; avoid foaming.
- Gently swirl/roll until dissolved (do not shake).
- Label concentration (1 mg/mL) and date; refrigerate at 2–8 °C (35.6–46.4 °F), protected from light.
Advanced / Post‑Cycle Support Approach
Route: Subcutaneous injection. Frequency: Daily or every other day for short cycles (limit to ≤14 consecutive days to avoid pituitary desensitization).
| Week/Phase | Dose per Injection (mcg) | Units (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Days 1–7 (Burst) | 200 mcg | 20 units (0.20 mL) |
| Days 8–14 (Taper) | 100 mcg | 10 units (0.10 mL) |
| Week 3+ (Optional Maintenance) | 100 mcg 2–3×/wk | 10 units (0.10 mL) |
Important: Limit consecutive daily dosing to ≤14 days. Extended continuous administration may lead to GnRH receptor desensitization and reduced LH/FSH response[4].
Supplies Needed
Plan based on a 4–8 week protocol with 2–3 injections per week.
-
Peptide Vials (Gonadorelin, 2 mg each):
- 4 weeks (100 mcg × 3/wk) ≈ 1 vial
- 6 weeks (100 mcg × 3/wk) ≈ 1 vial
- 8 weeks (150 mcg × 3/wk) ≈ 2 vials
-
Insulin Syringes (U‑100, 30‑ or 50‑unit preferred):
- Per week: 3 syringes
- 4 weeks: 12 syringes
- 6 weeks: 18 syringes
- 8 weeks: 24 syringes
-
Bacteriostatic Water (10 mL bottles): Use 2.0 mL per vial for reconstitution.
- 4–6 weeks (1 vial): 2 mL → 1 × 10 mL bottle
- 8 weeks (2 vials): 4 mL → 1 × 10 mL bottle
-
Alcohol Swabs: One for the vial stopper + one for the injection site each administration.
- Per week: 6 swabs (2/injection × 3 injections)
- 4 weeks: 24 swabs
- 6 weeks: 36 swabs
- 8 weeks: 48 swabs → recommend 1 × 100‑count box
Protocol Overview
Concise summary of the periodic micro‑dosing regimen.
- Goal: Stimulate endogenous LH and FSH release to support testosterone production and testicular function[1][5].
- Schedule: Subcutaneous injections 2–3 times weekly for 4–8 weeks; limit daily dosing to ≤14 consecutive days.
- Dose Range: 50–200 mcg per injection based on goals and response.
- Reconstitution: 2.0 mL per 2 mg vial (1 mg/mL) for accurate unit measurements.
- Storage: Lyophilized frozen; reconstituted refrigerated; avoid repeated freeze–thaw.
Dosing Protocol
Suggested periodic titration approach.
- Start: 50–100 mcg per injection; assess tolerance before increasing.
- Target: 100–150 mcg per injection, 2–3 times weekly.
- Frequency: Non‑consecutive days (e.g., Mon/Wed/Fri) to mimic pulsatile GnRH release.
- Cycle Length: 4–8 weeks; include off‑periods to maintain pituitary sensitivity.
- Timing: Morning injections preferred; rotate injection sites.
Storage Instructions
Proper storage preserves peptide quality.
- Lyophilized: Store at −20 °C (−4 °F) in dry, dark conditions; minimize moisture exposure.
- Reconstituted: Refrigerate at 2–8 °C (35.6–46.4 °F); use within 4 weeks and avoid freeze–thaw.
- Allow vials to reach room temperature before opening to reduce condensation uptake.
Important Notes
Practical considerations for consistency and safety.
- Use new sterile insulin syringes; dispose in a sharps container.
- Rotate injection sites (abdomen, thighs, upper arms) to reduce local irritation.
- Inject slowly; wait a few seconds before withdrawing the needle.
- Document each dose, date, and site rotation to maintain consistency.
- Limit continuous daily dosing to ≤14 days to prevent receptor desensitization[4].
How This Works
Gonadorelin is a synthetic decapeptide identical to endogenous gonadotropin‑releasing hormone (GnRH) secreted by the hypothalamus[1]. When administered in short, pulsatile fashion, it binds to GnRH receptors on pituitary gonadotrophs, triggering the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle‑stimulating hormone (FSH)[2][3]. LH stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone in men and triggers ovulation in women, while FSH supports spermatogenesis and ovarian follicle development[5]. Unlike continuous GnRH agonist administration, which desensitizes receptors and suppresses gonadotropins, brief periodic dosing preserves the natural pulsatile signaling pattern[4][6].
Potential Benefits & Side Effects
Observations from clinical and preclinical literature.
- Supports endogenous testosterone production by stimulating LH release[1][5].
- May help maintain testicular volume and function during exogenous testosterone therapy[7].
- Promotes spermatogenesis and fertility in hypogonadotropic hypogonadism when administered in pulsatile regimens[8][9].
- Generally well tolerated; occasional mild injection‑site reactions (redness, itching, or swelling) may occur[10].
- Possible transient headache or flushing shortly after injection[10].
Lifestyle Factors
Complementary strategies for best outcomes.
- Maintain adequate sleep (7–9 hours) to support natural hormonal rhythms.
- Pair with resistance training and balanced nutrition to optimize hormonal response.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques; chronic stress can impair HPG axis function.
- Avoid excessive alcohol and limit endocrine disruptors where possible.
Injection Technique
General subcutaneous guidance from clinical best‑practice resources[11].
- Clean the vial stopper and skin with alcohol; allow to dry.
- Pinch a skinfold; insert the needle at 45–90° into subcutaneous tissue[12][13].
- Do not aspirate for subcutaneous injections; inject slowly and steadily[12].
- Rotate sites systematically (abdomen, thighs, upper arms) to avoid lipohypertrophy[14].
Recommended Source
We recommend Pure Lab Peptides for high‑purity Gonadorelin (2 mg).
Why Pure Lab Peptides?
- High‑purity, third‑party‑tested lots with batch COAs.
- Consistent, ISO‑aligned handling and documentation.
- Reliable fulfillment to maintain cold‑chain integrity.
Important Note
This content is intended for therapeutic educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
References
-
PubMed
— GnRH agonists: gonadorelin, leuprolide, and nafarelin – overview of pharmacology and clinical applications -
Mayo Clinic
— Gonadorelin injection routes and indications for LH/FSH stimulation testing -
Wikipedia
— Gonadorelin pharmacology, pulsatile dosing, and clinical history -
PMC
— Gonadotropin‑releasing hormone analogs: pulsatile vs. continuous effects on FSH/LH -
PubMed
— Gonadotropin treatment for male hypogonadotropic hypogonadism – spermatogenesis and fertility -
ScienceDirect
— Gonadorelin agonist overview: initial stimulation and subsequent down‑regulation mechanisms -
PMC
— Preserving fertility in the hypogonadal patient: hCG and GnRH therapy options -
PMC
— Pulsatile gonadorelin pump induces earlier spermatogenesis in congenital HH men -
PubMed
— Application of GnRH in hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: diagnostic and therapeutic aspects -
Drugs.com
— Gonadorelin injectable: uses, side effects, and warnings -
PMC
— Subcutaneous drug injection review: pharmacologic considerations -
CDC
— Vaccine administration: subcutaneous route (angle/site; no aspiration) -
CDC (Subcut Injection PDF)
— Technique diagram and site guidance for subcutaneous injections -
NCBI Bookshelf
— Best practices for injection (asepsis, preparation, and administration) -
Pure Lab Peptides
— Gonadorelin (2 mg) product page (quality and batch documentation)