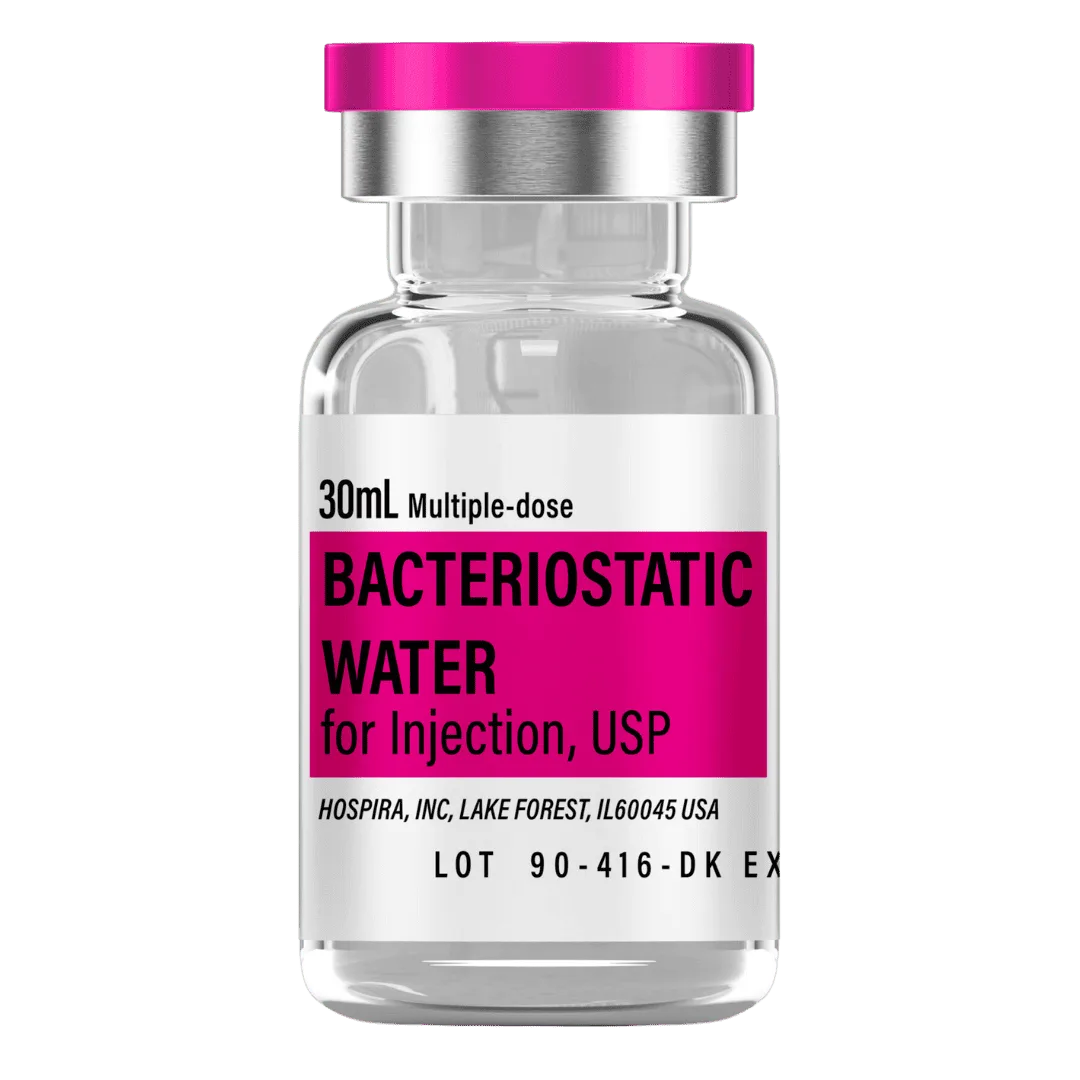DSIP (10 mg Vial) Dosage Protocol
Quickstart Highlights
DSIP dosage protocols can help promote deep, restorative delta-wave sleep and support healthy stress response. Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide (DSIP) is a naturally occurring nonapeptide (9 amino acids) first isolated from rabbit brain for its ability to enhance slow-wave sleep[1]. Research indicates DSIP may improve sleep quality, normalize sleep architecture, reduce stress-related cortisol patterns, and support mood stabilization without next-day grogginess[2][3]. This educational protocol presents a once-daily subcutaneous evening approach using a practical dilution for clear insulin-syringe measurements.
- Reconstitute: Add 3.0 mL bacteriostatic water → ~3.33 mg/mL concentration.
- Typical daily range: 100–300 mcg once daily in the evening (gradual titration).
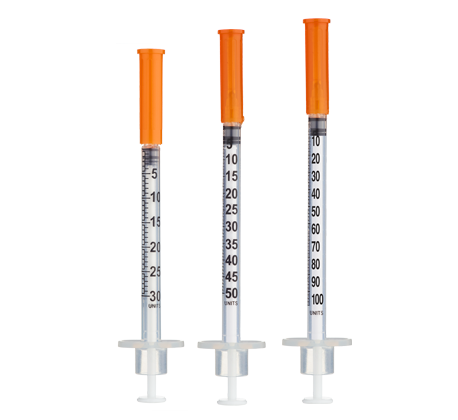
- Easy measuring: At 3.33 mg/mL, 1 unit = 0.01 mL ≈ 33.3 mcg on a U-100 insulin syringe.
- Storage: Lyophilized: freeze at −20 °C (−4 °F); after reconstitution, refrigerate at 2–8 °C (35.6–46.4 °F); avoid freeze–thaw cycles.

Dosing & Reconstitution Guide
Educational guide for reconstitution and nightly dosing
Standard / Gradual Approach (3 mL = ~3.33 mg/mL)
| Week | Daily Dose (mcg) | Units (per injection) (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | 100 mcg | 3 units (0.03 mL) |
| Week 2 | 150 mcg | 5 units (0.05 mL) |
| Week 3 | 200 mcg | 6 units (0.06 mL) |
| Weeks 4–8 | 250–300 mcg | 8–9 units (0.08–0.09 mL) |
Frequency: Inject once daily subcutaneously in the evening, approximately 30–60 minutes before bedtime[4]. For ≤10-unit (≤0.10 mL) administrations, consider 30- or 50-unit insulin syringes for improved readability.
Reconstitution Steps
- Draw 3.0 mL bacteriostatic water with a sterile syringe.
- Inject slowly down the vial wall; avoid foaming.
- Gently swirl/roll until dissolved (do not shake).
- Label and refrigerate at 2–8 °C (35.6–46.4 °F), protected from light.
Supplies Needed
Plan based on an 8–12 week nightly protocol with gradual titration.
-
Peptide Vials (DSIP, 10 mg each):
- 8 weeks ≈ 1 vial (10 mg supports ~33–100 doses at 100–300 mcg)
- 12 weeks ≈ 2 vials
-
Insulin Syringes (30- or 50-unit recommended for small volumes):
- Per week: 7 syringes (1/day)
- 8 weeks: 56 syringes
- 12 weeks: 84 syringes
-
Bacteriostatic Water (10 mL bottles): Use 3.0 mL per vial for reconstitution.
- 8 weeks (1 vial): 3 mL → 1 × 10 mL bottle
- 12 weeks (2 vials): 6 mL → 1 × 10 mL bottle
-
Alcohol Swabs: One for the vial stopper + one for the injection site each day.
- Per week: 14 swabs (2/day)
- 8 weeks: 112 swabs → recommend 2 × 100-count boxes
- 12 weeks: 168 swabs → recommend 2 × 100-count boxes
Protocol Overview
Concise summary of the once-daily evening regimen.
- Goal: Support improved sleep quality, enhanced delta-wave (slow-wave) sleep, and stress modulation over time[2][3].
- Schedule: Daily subcutaneous injections in the evening for 8–12 weeks.
- Dose Range: 100–300 mcg daily with gradual titration.
- Reconstitution: 3.0 mL per 10 mg vial (~3.33 mg/mL) for accurate unit measurements.
- Storage: Lyophilized frozen; reconstituted refrigerated; avoid repeated freeze–thaw.
Dosing Protocol
Suggested nightly titration approach.
- Start: 100 mcg nightly; increase by ~50 mcg every 1–2 weeks as tolerated.
- Target: 250–300 mcg nightly by Weeks 4–8.
- Frequency: Once per day (subcutaneous), 30–60 minutes before bedtime.
- Cycle Length: 8–12 weeks; consider a break after the cycle.
- Timing: Evening dosing to align with natural sleep onset; rotate injection sites.
Storage Instructions
Proper storage preserves peptide quality.
- Lyophilized: Store at −20 °C (−4 °F) in dry, dark conditions; minimize moisture exposure[5].
- Reconstituted: Refrigerate at 2–8 °C (35.6–46.4 °F); prepare aliquots if needed and avoid freeze–thaw.
- Allow vials to reach room temperature before opening to reduce condensation uptake.
Important Notes
Practical considerations for consistency and safety.
- Use new sterile insulin syringes; dispose in a sharps container.
- Rotate injection sites (abdomen, thighs, upper arms) to reduce local irritation[6].
- Inject slowly; wait a few seconds before withdrawing the needle.
- Document daily dose and site rotation to maintain consistency.
- Avoid other sedatives during DSIP use to clearly evaluate its effects on sleep.
How This Works
DSIP acts as a neuromodulator of the sleep-wake cycle and stress response. Administration consistently increases delta-wave (slow-wave) sleep in EEG recordings[2], suggesting it promotes the initiation and maintenance of deep, non-REM sleep. DSIP readily crosses the blood-brain barrier to exert central effects[7] and may enhance inhibitory neuronal activity or modulate sleep-regulating brain regions. Additionally, DSIP attenuates ACTH and corticosterone release in response to stress, indicating an effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis[8]. Unlike conventional sedatives, DSIP tends to normalize sleep architecture without next-day grogginess[3].
Potential Benefits & Side Effects
Observations from preclinical and clinical literature.
- Supports improved sleep quality and increased slow-wave (delta) sleep duration[2][3].
- May help normalize disrupted sleep patterns in chronic insomnia[3].
- Shows potential for stress reduction and mood support through HPA axis modulation[8][9].
- Remarkably safe profile: animal studies found no lethal dose even at extremely high doses; human studies report only mild, transient side effects (occasional headache or nausea)[1][8].
- Occasional mild injection-site reactions (redness/itch) may occur with subcutaneous administration.
Lifestyle Factors
Complementary strategies for best outcomes.
- Maintain consistent sleep-wake schedules to reinforce circadian rhythm.
- Limit caffeine and screen exposure in the evening hours.
- Create a dark, cool sleep environment to support natural melatonin production.
- Prioritize stress management techniques and regular physical activity during daytime hours.
Injection Technique
General subcutaneous guidance from clinical best-practice resources[6][10].
- Clean the vial stopper and skin with alcohol; allow to dry.
- Pinch a skinfold; insert the needle at 45–90° into subcutaneous tissue[6].
- Do not aspirate for subcutaneous injections; inject slowly and steadily.
- Rotate sites systematically (abdomen, thighs, upper arms) to avoid lipohypertrophy[10].
- Using a 30- or 50-unit insulin syringe improves accuracy when measuring small volumes (3–9 units).
Recommended Source
We recommend Pure Lab Peptides for high-purity DSIP (10 mg).
Why Pure Lab Peptides?
- High-purity, third-party-tested lots with batch COAs.
- Consistent, ISO-aligned handling and documentation.
- Reliable fulfillment to maintain cold-chain integrity.
Important Note
This content is intended for therapeutic educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
References
-
European Journal of Anaesthesiology
— Delta sleep-inducing peptide: discovery, structure, and pharmacological overview -
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews (PubMed)
— Delta-sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP): a review of sleep-promoting and neuromodulatory effects -
European Neurology (PubMed)
— Effects of delta-sleep-inducing peptide on 24-hour sleep-wake behaviour in severe chronic insomnia -
European Neurology (PubMed)
— DSIP in insomnia: timing and frequency of administration in clinical trials -
Tocris Bioscience
— Stability and storage guidelines for research peptides -
MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine)
— Subcutaneous (SQ) injections: technique, site selection, and procedure -
Frontiers in Pharmacology
— DSIP fusion peptides crossing the blood-brain barrier and efficacy in insomnia models -
European Neurology (PubMed)
— Therapeutic effects of delta-sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP) in patients with chronic pain episodes -
European Neurology (PubMed)
— DSIP in the treatment of withdrawal syndromes from alcohol and opiates -
Johns Hopkins Arthritis Center
— How to give a subcutaneous injection: site rotation and best practices -
European Neurology (PubMed)
— Effects of delta sleep-inducing peptide on sleep of chronic insomniac patients (double-blind study) -
CDC
— Vaccine administration: subcutaneous route (angle/site guidance) -
NCBI Bookshelf
— Best practices for injection (asepsis, preparation, and administration) -
Subcutaneous Drug Injection Review (PMC)
— Pharmacologic considerations of the subcutaneous route -
Pure Lab Peptides
— DSIP (10 mg) product page (quality and batch documentation)