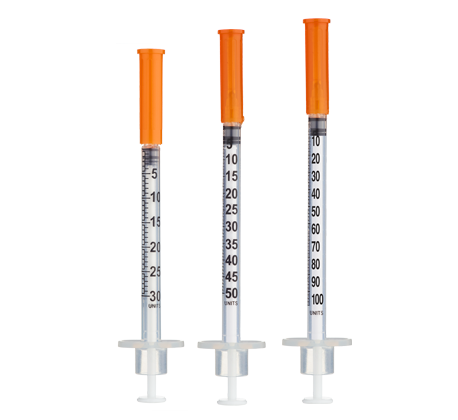
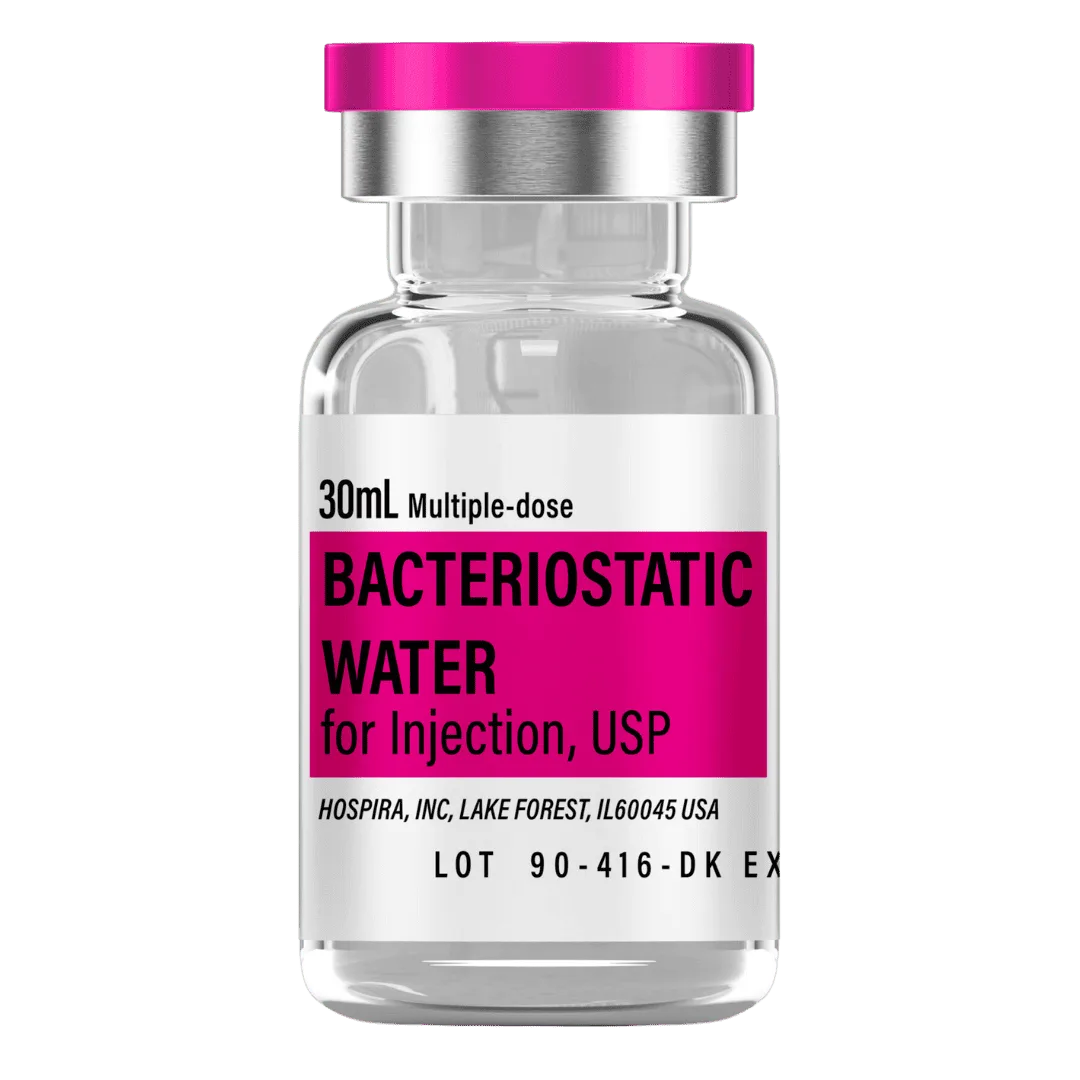CJC-1295 NO DAC (5 mg Vial) Dosage Protocol
Quickstart Highlights
CJC-1295 NO DAC dosage protocols leverage this synthetic 29‑amino‑acid GHRH analog (also known as Modified GRF 1–29 or Mod GRF) to stimulate natural, pulsatile growth hormone secretion from the pituitary gland[1][2]. Unlike exogenous GH administration, CJC-1295 NO DAC preserves the body’s physiologic feedback loop, supporting enhanced GH and IGF‑1 levels while maintaining natural hormonal rhythms[3][4]. Research suggests benefits may include improved body composition, enhanced recovery, better sleep quality, and support for lean muscle mass and metabolic function[5][6]. This educational protocol presents a practical once‑daily subcutaneous approach using a dilution optimized for clear insulin‑syringe measurements.
- Reconstitute: Add 3.0 mL bacteriostatic water → ~1.67 mg/mL concentration.
- Typical daily range: 100–300 mcg once daily (gradual titration).
- Easy measuring: At 1.67 mg/mL, 1 unit = 0.01 mL ≈ 16.7 mcg on a U‑100 insulin syringe.
- Storage: Lyophilized: refrigerate at 2–8 °C (35.6–46.4 °F); after reconstitution, refrigerate and use within 1–2 weeks; for longer storage, freeze at ≤−20 °C (≤−4 °F).

Dosing & Reconstitution Guide
Educational guide for reconstitution and daily dosing
Standard / Gradual Approach (3 mL = ~1.67 mg/mL)
| Week | Daily Dose (mcg) | Units (per injection) (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Weeks 1–2 | 100 mcg | 6 units (0.06 mL) |
| Weeks 3–4 | 150 mcg | 9 units (0.09 mL) |
| Weeks 5–6 | 200 mcg | 12 units (0.12 mL) |
| Weeks 7–12 | 250–300 mcg | 15–18 units (0.15–0.18 mL) |
Frequency: Inject once daily subcutaneously, typically at bedtime to align with natural nocturnal GH pulsatility[2][3]. For ≤10‑unit (≤0.10 mL) administrations (Weeks 1–4), consider 30‑ or 50‑unit insulin syringes for improved readability.
Reconstitution Steps
- Draw 3.0 mL bacteriostatic water with a sterile syringe.
- Inject slowly down the vial wall; avoid foaming.
- Gently swirl/roll until dissolved (do not shake).
- Label and refrigerate at 2–8 °C (35.6–46.4 °F), protected from light.
Supplies Needed
Plan based on an 8–12 week daily protocol with gradual titration.
-
Peptide Vials (CJC-1295 NO DAC, 5 mg each):
- 8 weeks ≈ 2 vials
- 12 weeks ≈ 3 vials
- 16 weeks ≈ 4 vials
-
Insulin Syringes (U‑100):
- Per week: 7 syringes (1/day)
- 8 weeks: 56 syringes
- 12 weeks: 84 syringes
- 16 weeks: 112 syringes
-
Bacteriostatic Water (10 mL bottles): Use ~3.0 mL per vial for reconstitution.
- 8 weeks (2 vials): 6 mL → 1 × 10 mL bottle
- 12 weeks (3 vials): 9 mL → 1 × 10 mL bottle
- 16 weeks (4 vials): 12 mL → 2 × 10 mL bottles
-
Alcohol Swabs: One for the vial stopper + one for the injection site each day.
- Per week: 14 swabs (2/day)
- 8 weeks: 112 swabs → recommend 2 × 100‑count boxes
- 12 weeks: 168 swabs → recommend 2 × 100‑count boxes
- 16 weeks: 224 swabs → recommend 3 × 100‑count boxes
Protocol Overview
Concise summary of the once‑daily regimen.
- Goal: Stimulate pulsatile GH release and elevate IGF‑1 levels to support body composition, recovery, and overall metabolic health[2][5].
- Schedule: Daily subcutaneous injections for 8–12 weeks (extend to 16 weeks if desired).
- Dose Range: 100–300 mcg daily with gradual titration.
- Reconstitution: 3.0 mL per 5 mg vial (~1.67 mg/mL) for accurate unit measurements.
- Storage: Lyophilized refrigerated or frozen; reconstituted refrigerated; avoid repeated freeze–thaw.
Dosing Protocol
Suggested daily titration approach.
- Start: 100–150 mcg daily; increase by ~50 mcg every 1–2 weeks as tolerated.
- Target: 200–300 mcg daily by Weeks 5–12.
- Frequency: Once per day (subcutaneous), preferably at bedtime.
- Cycle Length: 8–12 weeks; optional extension to 16 weeks.
- Timing: Administer at bedtime to align with natural nocturnal GH pulses; rotate injection sites.
Storage Instructions
Proper storage preserves peptide quality.
- Lyophilized: Store at 2–8 °C (35.6–46.4 °F); for extended storage, freeze at ≤−20 °C (≤−4 °F); minimize moisture exposure.
- Reconstituted: Refrigerate at 2–8 °C (35.6–46.4 °F); use within 1–2 weeks; avoid freeze–thaw cycles.
- Allow vials to reach room temperature before opening to reduce condensation uptake.
Important Notes
Practical considerations for consistency and safety.
- Use new sterile insulin syringes; dispose in a sharps container.
- Rotate injection sites (abdomen, thighs, upper arms) to reduce local irritation.
- Inject slowly; wait a few seconds before withdrawing the needle.
- Document daily dose and site rotation to maintain consistency.
- Administer on an empty stomach (fasted for ≥2 hours) to optimize GH response.
How This Works
CJC-1295 NO DAC (Modified GRF 1–29) is a truncated GHRH analog with four amino acid substitutions (D‑Ala2, Gln8, Ala15, Leu27) that enhance stability against enzymatic degradation[1]. It binds to GHRH receptors on pituitary somatotrophs, stimulating the synthesis and pulsatile release of endogenous growth hormone[2][3]. Unlike exogenous GH administration, GHRH analogs preserve the physiologic feedback loop, resulting in more natural GH pulsatility without the risks associated with supraphysiological GH levels[7]. The short half‑life (~30 minutes) produces discrete GH pulses that mimic the body’s natural secretion pattern[1][4].
Potential Benefits & Side Effects
Observations from preclinical and clinical literature on GHRH analogs.
- Stimulates pulsatile GH release and elevates IGF‑1 levels with chronic administration[2][5][6].
- May support improvements in body composition, including increased lean mass and reduced fat mass[8][9].
- May enhance recovery, sleep quality, and overall energy levels[10].
- Generally well tolerated; occasional mild side effects may include injection‑site reactions (redness, swelling), transient flushing, or headache[11].
Lifestyle Factors
Complementary strategies for best outcomes.
- Pair with a balanced, protein‑forward diet tailored to energy needs.
- Combine resistance training and aerobic activity to reinforce metabolic adaptations and GH response.
- Prioritize sleep and stress management to support natural GH pulsatility and recovery.
- Administer peptide in a fasted state to maximize GH release.
Injection Technique
General subcutaneous guidance from clinical best‑practice resources[12].
- Clean the vial stopper and skin with alcohol; allow to dry.
- Pinch a skinfold; insert the needle at 45–90° into subcutaneous tissue[12][13].
- Do not aspirate for subcutaneous injections; inject slowly and steadily[12].
- Rotate sites systematically (abdomen, thighs, upper arms) to avoid lipohypertrophy[14].
Recommended Source
We recommend Pure Lab Peptides for high‑purity CJC-1295 NO DAC (5 mg).
Why Pure Lab Peptides?
- High‑purity, third‑party‑tested lots with batch COAs.
- Consistent, ISO‑aligned handling and documentation.
- Reliable fulfillment to maintain cold‑chain integrity.
Important Note
This content is intended for therapeutic educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
References
-
Wikipedia
— Modified GRF (1–29): structure, amino acid substitutions, and pharmacokinetics -
Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (2006)
— Teichman et al.: Prolonged stimulation of GH and IGF‑I by CJC-1295 in healthy adults -
American Journal of Physiology (2006)
— Alba et al.: Once‑daily CJC-1295 normalizes growth in GHRH knockout mice -
Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (2006)
— Veldhuis et al.: Pulsatile GH secretion persists during continuous CJC-1295 stimulation -
PMC
— Growth Hormone Secretagogue Treatment in Hypogonadal Men Raises Serum IGF‑1 Levels -
PMC
— Effects of GHRH Analog (Tesamorelin) on Endogenous GH Pulsatility and Insulin Sensitivity -
PMC
— Sermorelin: a better approach to management of adult‑onset growth hormone insufficiency -
PMC
— Beyond the androgen receptor: role of GHS in body composition in hypogonadal males -
PMC
— The Safety and Efficacy of Growth Hormone Secretagogues (Review) -
PMC
— GHRH Effects on Brain GABA Levels in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Healthy Aging -
PubMed
— Sermorelin: review of its use in diagnosis and treatment of GH deficiency -
CDC
— Vaccine administration: subcutaneous route (angle/site; no aspiration) -
CDC (Subcut Injection PDF)
— Technique diagram and site guidance for subcutaneous injections -
NCBI Bookshelf
— Best practices for injection (asepsis, preparation, and administration) -
Subcutaneous Drug Injection Review (PMC)
— Pharmacologic considerations of the subcutaneous route -
Pure Lab Peptides
— CJC-1295 NO DAC (5 mg) product page (quality and batch documentation)