Cerebrolysin (60 mg Vial) Dosage Protocol
Quickstart Highlights
Cerebrolysin dosage protocols leverage this porcine brain-derived neuropeptide preparation containing low-molecular-weight peptides and free amino acids that cross the blood–brain barrier to support neuronal survival and neuroplasticity[1]. By mimicking endogenous neurotrophic factors such as nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), Cerebrolysin may enhance cognitive function, support memory, and promote neuroprotection in age-related cognitive decline and stroke recovery[2][3]. This educational protocol presents a once- to twice-daily subcutaneous approach using a practical dilution for clear insulin-syringe measurements.
- Reconstitute: Add 3.0 mL bacteriostatic water to the 60 mg vial → 20 mg/mL concentration.
- Typical daily range: 20–32 mg once or twice daily (gradual titration over 3–4 weeks).
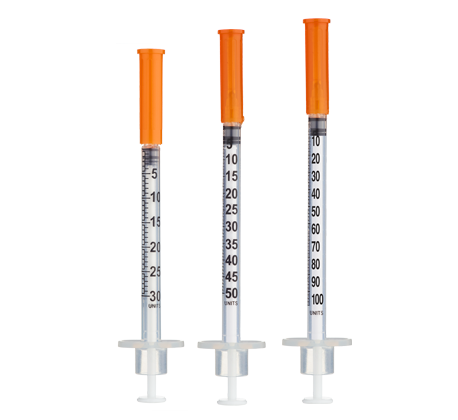
- Easy measuring: At 20 mg/mL, 1 unit = 0.01 mL = 200 mcg (0.2 mg) on a U-100 insulin syringe.
- Storage: Lyophilized: store at ≤25 °C (77 °F) in dry, dark conditions; after reconstitution, refrigerate at 2–8 °C (36–46 °F) and use within 7 days. Do not freeze reconstituted solution.

Dosing & Reconstitution Guide
Educational guide for reconstitution and daily dosing
Standard / Gradual Titration Schedule (3 mL = 20 mg/mL)
| Week | Daily Dose (mg) | Injection Schedule (Units & mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | 20 mg | 100 units (1.0 mL) once each morning |
| Week 2 | 24 mg | 60 units (0.6 mL) AM + 60 units (0.6 mL) PM |
| Week 3 | 28 mg | 70 units (0.7 mL) AM + 70 units (0.7 mL) PM |
| Week 4+ | 32 mg | 80 units (0.8 mL) AM + 80 units (0.8 mL) PM |
Frequency: Inject once daily subcutaneously in Week 1, then twice daily (morning and evening) from Week 2 onward to keep each injection ≤1.0 mL for optimal absorption[4]. Morning administration is preferred for once-daily dosing due to Cerebrolysin’s mildly stimulatory properties[5].
Reconstitution Steps
- Draw 3.0 mL bacteriostatic water with a sterile syringe.
- Inject slowly down the vial wall; avoid foaming.
- Gently swirl/roll until dissolved (do not shake).
- Label with date/time and refrigerate at 2–8 °C (36–46 °F); use within 7 days.
Supplies Needed
Plan based on an 8–16 week daily protocol with gradual titration to 32 mg/day maintenance.
-
Peptide Vials (Cerebrolysin, 60 mg each):
- 8 weeks ≈ 28 vials
- 12 weeks ≈ 42 vials
- 16 weeks ≈ 58 vials
-
Insulin Syringes (U-100, 1 mL):
- Week 1: 7 syringes (1/day)
- Weeks 2+: 14 syringes/week (2/day)
- 8 weeks: ~105 syringes
- 12 weeks: ~161 syringes
- 16 weeks: ~217 syringes
-
Bacteriostatic Water (10 mL bottles): Use 3.0 mL per vial for reconstitution.
- 8 weeks (28 vials): 84 mL → 9 × 10 mL bottles
- 12 weeks (42 vials): 126 mL → 13 × 10 mL bottles
- 16 weeks (58 vials): 174 mL → 18 × 10 mL bottles
-
Alcohol Swabs: Two per injection (vial stopper + skin).
- 8 weeks (~105 injections): ~210 swabs → 3 × 100-count boxes
- 12 weeks (~161 injections): ~322 swabs → 4 × 100-count boxes
- 16 weeks (~217 injections): ~434 swabs → 5 × 100-count boxes
Protocol Overview
Concise summary of the daily regimen.
- Goal: Promote neuroprotection and neuronal survival by providing neurotrophic support via NGF/BDNF-mimetic activity[1][6].
- Schedule: Daily subcutaneous injections for 8–12 weeks (extend to 16 weeks if desired); clinical practice often uses multiple cycles per year[5].
- Dose Range: 20–32 mg per day with gradual titration over 3–4 weeks.
- Reconstitution: 3.0 mL per 60 mg vial (20 mg/mL) for precise measurements.
- Storage: Lyophilized at room temp; reconstituted refrigerated; never freeze after mixing.
Dosing Protocol
Stepwise daily titration approach.
- Start: 20 mg/day (100 units once daily in the morning).
- Titration: Increase by ~4 mg (~20 units) each week as tolerated.
- Target: 28–32 mg daily by Week 4, split into AM and PM doses.
- Frequency: Once daily (Week 1); twice daily (Weeks 2+) when volume exceeds 1.0 mL.
- Timing: Morning for once-daily; morning and late afternoon/early evening for split doses.
Storage Instructions
Proper storage preserves peptide quality.
- Lyophilized: Store at ≤25 °C (77 °F) in dry, dark conditions; refrigeration (2–8 °C) also acceptable.
- Reconstituted: Refrigerate at 2–8 °C (36–46 °F); use within 7 days; do not freeze.
- Allow vials to reach room temperature before injection to reduce discomfort; protect from light.
Important Notes
Practical considerations for consistency and safety.
- Use new sterile insulin syringes for each injection; dispose in a sharps container.
- Rotate injection sites (abdomen, thighs, upper arms) to prevent lipohypertrophy[7].
- Inject slowly (over 5–10 seconds for 1 mL); wait 5–10 seconds before withdrawing needle.
- Keep each single injection ≤1.0 mL; split larger daily doses into two administrations.
- Document daily dose, time, and site rotation to maintain consistency.
How This Works
Cerebrolysin consists of enzymatically prepared low-molecular-weight neuropeptides (below 10 kDa) and free amino acids derived from porcine brain tissue[1]. These components can cross the blood–brain barrier and exert multimodal neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects by mimicking endogenous growth factors such as NGF and BDNF[6]. Preclinical and clinical studies suggest Cerebrolysin supports neuronal survival, enhances synaptic plasticity, modulates neuroinflammatory pathways, and may promote functional recovery following stroke or traumatic brain injury[3][8].
Potential Benefits & Side Effects
Observations from preclinical and clinical literature.
- Clinical trials report improvements in cognitive function and global clinical impression in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia[2][9].
- Meta-analyses in acute ischemic stroke suggest improved neurological recovery at 1–3 months post-stroke[3].
- Generally well-tolerated with a safety profile similar to placebo in controlled studies; adverse event rates comparable between treatment and placebo groups[9].
- Most common side effects are mild and transient: headache, dizziness, or agitation in a minority of patients[2].
- Subcutaneous administration may cause mild injection-site reactions (redness, itching); proper technique and site rotation minimize this risk.
Lifestyle Factors
Complementary strategies for optimal brain health.
- Maintain a brain-healthy diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and B-vitamins to support neuronal membrane health.
- Engage in regular aerobic exercise (30+ minutes most days) to naturally increase endogenous BDNF and enhance neuroplasticity.
- Challenge cognitive function daily through puzzles, learning new skills, reading, or social engagement.
- Prioritize quality sleep (7–9 hours) and stress management to support neural recovery and memory consolidation.
- Avoid excessive alcohol and other neurotoxins that can counteract neuroprotective benefits.
Injection Technique
General subcutaneous guidance from clinical best-practice resources[10][11].
- Clean the vial stopper and skin with alcohol; allow to dry completely.
- Pinch a 1–2 inch skinfold; insert needle at 45–90° into subcutaneous tissue[10].
- Do not aspirate for subcutaneous injections; inject slowly and steadily over 5–10 seconds[11].
- Wait 5–10 seconds after injection before withdrawing; dispose of syringe immediately in sharps container.
- Rotate sites systematically (abdomen quadrants, thighs, upper arms) to prevent tissue damage[7].
Recommended Source
We recommend Pure Lab Peptides for high-purity Cerebrolysin (60 mg).
Why Pure Lab Peptides?
- High-purity (≥99%), third-party-tested lots with batch COAs available.
- Strict ISO-aligned handling and storage protocols to preserve peptide integrity.
- Reliable fulfillment with temperature-controlled shipping when needed.
Important Note
This content is for educational purposes only and is not medical advice. Cerebrolysin is not FDA-approved in the U.S. for clinical use; any application should comply with applicable laws and ethical research practices.
References
-
International Peptide Society
— Cerebrolysin Monograph: mechanism, pharmacology, and clinical applications (2018) -
Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation
— Cerebrolysin Cognitive Vitality Report: efficacy and safety in dementia (2016) -
Journal of Clinical Medicine (MDPI)
— Role and impact of Cerebrolysin for ischemic stroke care: systematic review and meta-analysis -
PMC – Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Review
— Pharmacologic considerations of the subcutaneous route (absorption, dispersion, volume limits) -
Ever Neuro Pharma
— Cerebrolysin Treatment Handbook: dosing, timing, storage, and clinical protocols (2023) -
Frontiers in Neuroscience (PMC)
— Neurotrophic factors and neurodegeneration: role of NGF/BDNF pathways in neuroprotection -
PMC – Injection Technique Factor
— Site rotation and lipohypertrophy prevention in repeated subcutaneous injections -
PLOS One
— Neuroprotective action of Cerebrolysin in acute and chronic brain ischemia (rat models, 2021) -
PubMed
— A 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of three dosages of Cerebrolysin in mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease -
NCBI Bookshelf
— Chapter 18: Administration of Parenteral Medications (subcutaneous technique, angle, site selection) -
CDC
— Vaccine Administration: Subcutaneous Injection technique and best practices -
Pure Lab Peptides
— Cerebrolysin (60 mg) product page (quality specifications and batch documentation)